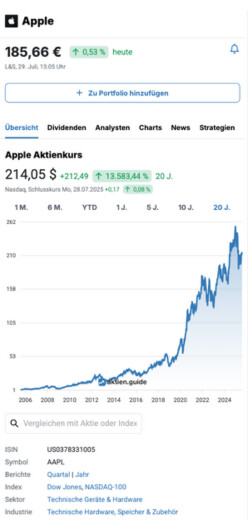
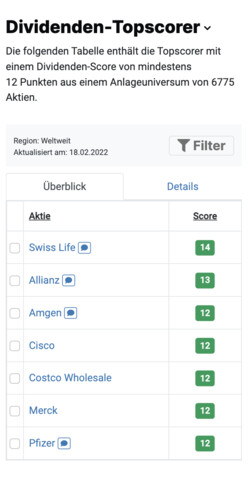
Elite Dividend Stocks 2025 - Germany, Europe and USA
The Best Dividend Stocks are analyzed daily from a stock universe of 7,088. In doing so, 64 countries, 74 sectors and 33 indices are analysed. The minimum requirement is 5 dividend payments in a row without a cut.
Germany
Austria
Switzerland
Eurozone
Europe ex Euro
United States
Excerpt from a Elite Dividend Stock list for a dividend portfolio
The table shows the top 5 dividend stocks from the Dividendenadel list of German blue chips. In this list you will find all German large and mid cap stocks(market capital ization > € 2 billion). All small cap stocks( market capitalization < € 2 billion) can be found in the list Germany second-line stocks. The explanations of the key metrics and abbreviations can be found here.
| Stock | Div. Score | Market Cap. | Always increased | Never lowered | Always paid | Growth 1Y |
Growth 5Y |
Growth 10Y |
Div. Yield current Current Dividend Yield |
Div. return 5Y Dividend Yield 5Y |
Payout 3Y |
|---|
Elite Dividend Stock Metrics in Detail
Below you will find an overview of the Elite Dividend Stock Metrics. Each metric is explained in detail and why they are important.
Dividend Series: Dividend Increases (Always Increased), Dividend Consistency (Never Lowered) & Dividend Payments (Always Paid)
When considering dividend series, a distinction is made between 3 variants:
Dividend Increases (always increased)
The column Always Increased shows the number of consecutive years in which the company has increased its dividend.
Dividend Continuity (never reduced)
The Never Reduced column shows the dividend continuity. This refers to the number of consecutive years in which the company has not reduced its dividend. A constant dividend has a positive effect on dividend continuity, while a dividend cut has a negative effect.
Dividend Payments (always paid)
Always Paid is the number of consecutive years in which the company has paid a dividend. Dividend increases and dividend cuts are not taken into account here. Only the payment of a dividend is relevant.
Special Dividends are only included if the dividend series under consideration (Always Increased, Never Lowered or Always paid) would improve. In general, the higher the value of dividend increases (Always increased), dividend continuity (Never Lowered) or dividend payments (Always paid), the better. As the last 25 years are considered, the maximum value is 25.
Why are dividend series important?
Companies that continuously pay a dividend without having reduced it are often very solid dividend stocks. If the dividend has also been regularly increased, this indicates a great business model. This gives you a quick impression of the reliability of the dividend.
Dividend Growth: 1, 5 and 10 years
In addition to the continuous payment of dividends, growth plays a key role in selecting the best dividend stocks. In order to better classify Dividend Growth, we look at three time periods:
Dividend Growth 1 year
The Dividend Growth 1 year results from the change in the dividend compared to the previous financial year.
Dividend Growth 5 years and 10 years
For Dividend Growth over 5 and 10 years, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is calculated. To calculate this, the dividend payment for the completed financial year is first divided by the dividend payment for the financial year 5 or 10 years ago. The fifth or tenth root is then taken from the quotient.
Special Dividends are not included in the calculation.
Why is Dividend Growth important?
High Dividend Growth can be a significant lever for your return. Let's assume a company pays a dividend of €1 per share and increases the dividend by 15% for 5 consecutive years. After 5 years, you will already receive € 2 per share, i.e. twice as much as at the beginning!
Dividend yield: 5 years
The dividend yield 5 years describes the average dividend yield of the past 5 financial years. It is calculated as the quotient of the average of the dividend payments and the average of the stock market closing prices of the last 5 financial years. Special dividends are not included in the calculation.
Why is the 5-year dividend yield important?
The 5-year dividend yield helps you to better assess the dividend yield of a company. The current dividend yield is much more susceptible to fluctuation. This effect is somewhat reduced with the average of the last 5 years.
Payout or payout ratio: 1 and 3 years
Payout is the payout ratio, i.e. how much of the profit is distributed to shareholders in the form of a dividend (as a percentage). In order to better classify the payout, we look at two periods:
Payout 1 year
The payout 1 year results from the change in dividend payments in relation to earnings per share(EPS) compared to the previous financial year.
Payout 3Y
The 3-year payout is the payout ratio smoothed over 3 years. It is calculated by dividing the total of all dividend payments by the cumulative earnings per share for the last 3 financial years.
Why is the payout or payout ratio important?
The payout ratio tells you how much of the profit generated is paid out as dividends. A low payout ratio indicates that there is still room for dividend increases. A high payout ratio, on the other hand, can be seen as a warning signal. If too much money is paid out, the company may lack the funds for important investments.
Register for Free
StocksGuide is the ultimate tool for easily finding, analyzing and tracking stocks. Learn from successful investors and make informed investment decisions. We empower you to become a confident, independent investor.