Elite Dividend Stocks 2025 - Germany, Europe and USA
The Best Dividend Stocks are analyzed daily from a stock universe of 7,019. In doing so, 64 countries, 74 sectors and 33 indices are analysed. The minimum requirement is 5 dividend payments in a row without a cut.
Lithuania - Elite Dividend Stocks | Large Cap, Mid Cap and Small Cap
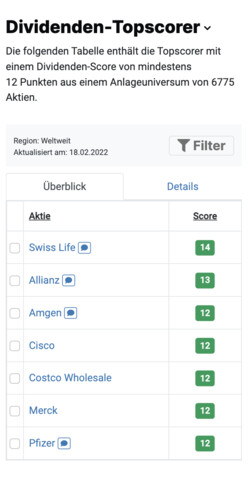
There are currently 0 large, mid and small cap stocks with a dividend continuity of 25 years. The table of solid dividend stocks is first sorted according to dividend continuity (never lowered). The current dividend yield is then considered.
| Stock | Div. Score | Market Cap. | Always increased | Never lowered | Always paid | Growth 1Y |
Growth 5Y |
Growth 10Y |
Div. Yield current Current Dividend Yield |
Div. return 5Y Dividend Yield 5Y |
Payout 3Y |
|---|
Lithuania - Elite Dividend Stocks | Large Cap, Mid Cap and Small Cap
There are currently 0 large, mid and small cap stocks with a dividend continuity of 25 years. The table of solid dividend stocks is first sorted according to dividend continuity (never lowered). The current dividend yield is then considered.
Elite Dividend Stock Metrics in Detail
Dividend increases (always increased)
The column Always increased shows the number of consecutive years in which the company has increased its dividend. Always increased means dividend increase.
Dividend continuity (never reduced)
The Never reduced column shows the dividend continuity. This refers to the number of consecutive years in which the company has not reduced its dividend. A constant dividend has a positive effect on dividend continuity, while a dividend cut has a negative effect.
Dividend payments (always paid)
Always paid is the number of consecutive years in which the company has paid a dividend. Dividend increases and dividend cuts are not taken into account here. Only the payment of a dividend plays a role.
Dividend growth: 1, 5 & 10 years
The Dividend Growth 1 year results from the change in the dividend compared to the previous financial year.
For Dividend Growth over 5 and 10 years, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is calculated. To calculate this, the dividend payment for the completed financial year is first divided by the dividend payment for the financial year 5 or 10 years ago. The fifth or tenth root is then taken from the quotient.
Dividend yield: 5 years
The dividend yield 5 years describes the average dividend yield of the past 5 financial years. It is calculated as the quotient of the average dividend payment and the average closing price of the last 5 financial years.
Payout: 1 & 3 years
The payout 1 year results from the change in dividend payments in relation to earnings per share(EPS) compared to the previous financial year.
The 3-year payout is the payout ratio smoothed over 3 years. It is calculated by dividing the total of all dividend payments by the cumulative earnings per share for the last 3 financial years.
Register for Free
StocksGuide is the ultimate tool for easily finding, analyzing and tracking stocks. Learn from successful investors and make informed investment decisions. We empower you to become a confident, independent investor.